Emerging Pollutants
Emerging Pollutants
Emerging Pollutants
Emerging pollutants, also known as Emerging Contaminants (ECs) or, in some scientific references, Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CECs), appear as chemical or biological compounds, whether natural or synthetic, that were not previously subject to regulation but have become an increasing concern due to their environmental and health impacts. These pollutants encompass a wide range of substances that can be found in water, soil, air, and even the food chain.
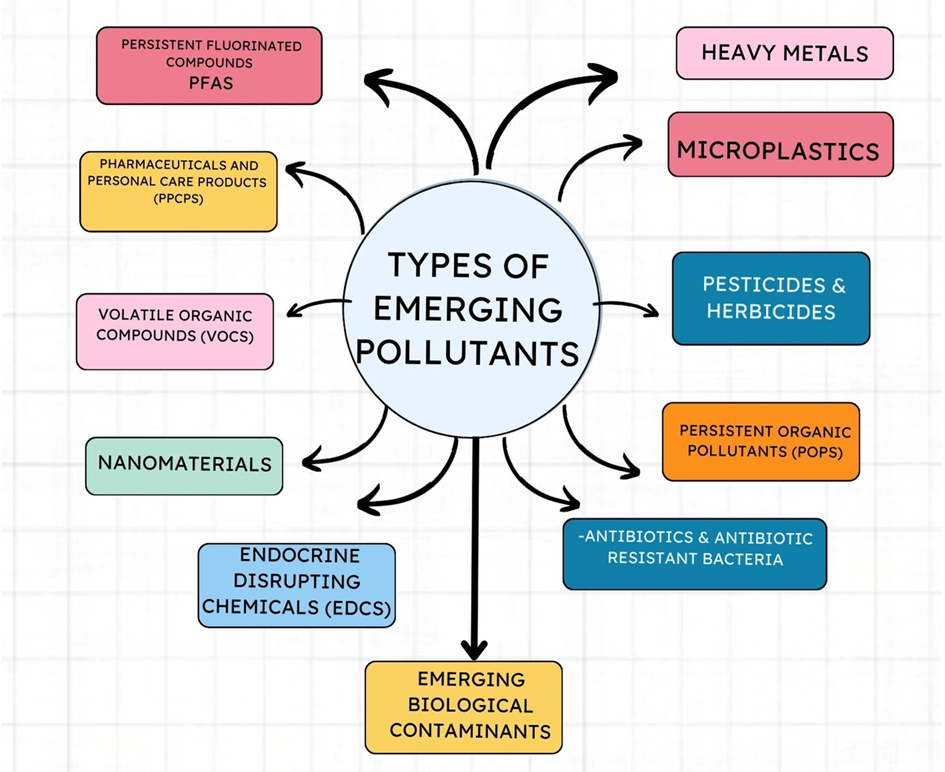
Comprehensive classification of emerging pollutants
- Persistent Fluorinated Compounds (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances – PFAS)
- Includes substances like PFOA and PFOS, used in water- and oil-resistant products, which remain in the environment for long periods.
- Microplastics (MPs)
- Plastic particles smaller than 5 mm, resulting from the degradation of plastic products, spread in aquatic environments, and are consumed by marine organisms, leading to bioaccumulation in the food chain. Their effects on human health and living organisms are still unknown.
- Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs)
- Includes drugs like antibiotics, painkillers, hormones, as well as products like disinfectants and perfumes. These reach the environment through wastewater, impacting aquatic systems and wildlife, contributing to antibiotic resistance.
- Pesticides & Herbicides
- Includes compounds like glyphosate and DDE, used in agriculture, causing soil and water contamination with negative effects on biodiversity and human health.
- Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
- Includes substances like dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), which persist in the environment for extended periods, accumulate in living organisms, and cause toxic effects.
- Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs)
- Includes compounds like bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, which affect the endocrine system of living organisms, leading to reproductive and developmental issues.
- Nanomaterials
- Nanoparticles used in medical and technological industries. Their effects on the environment and human health are not fully understood.
- Antibiotics & Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- The use of antibiotics in medicine and agriculture leads to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a public health threat. These bacteria can spread through wastewater into the environment.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
- Includes compounds like benzene and toluene, used in petrochemical industries, causing air pollution and impacting respiratory health.
- Heavy Metals
- Includes lead, mercury, and cadmium, produced from industrial and mining activities. They accumulate in soil and water, causing toxicity to living organisms.
- Emerging Biological Contaminants
- Includes bacteria, viruses, and harmful algae, which spread through water and food, leading to disease outbreaks.
TYPES